CBD is a popular compound that has potential health benefits. Some of the many uses of CBD oil products include anxiety relief, pain relief, and reduction of seizures.
CBD offers different benefits without causing a high. For this reason, we’ve seen it become a popular treatment option for many health conditions. Although CBD is growing increasingly, it’s still a complex compound to understand.
Here we answer one of the most asked questions – how CBD works in the human body
Read on to learn about the effects of CBD and how it offers numerous potential benefits.
What is CBD?
The cannabis plant has over 150 compounds called cannabinoids. CBD, or cannabidiol, is one of the many cannabinoids present in cannabis.
As one of the plant’s major cannabinoids, CBD makes up about 40% of its extract. CBD doesn’t produce any intoxicating effects. Some studies suggest that it may decrease the effects of THC when you take them together.
THC, short for tetrahydrocannabinol, is a cannabinoid responsible for the euphoric high people associate with cannabis.
How Does CBD Work in the Human Body?
We know CBD is a potential solution to various health issues. But, how CBD works in the human body?
CBD exerts its effects through different pathways. When you consume CBD, it interacts with your endocannabinoid system and helps complement its activities. However, CBD doesn’t bind directly with CB1 and CB2 receptors of this system.
In addition, CBD also interacts with non-cannabinoid receptors, making it a possible treatment option for many conditions. Some of the non-cannabinoid receptors CBD interacts with to produce its many effects include:
TRPV1: This receptor mediates a range of therapeutic effects. It plays a role in how we sense pain. It also regulates our body temperature.
Anandamide: The body produces this molecule on demand. It functions as a neurotransmitter. Anandamide plays a role in different bodily processes, including pain, pleasure, sleep, mood, dopamine levels, and many others.
PPARS Receptor: PPARS is a multi-role receptor, and CBD interacts with it as an agonist. A 2011 review examined the effects of PPARS agonists in conditions such as pain, inflammation, diabetes, neurodegenerative disorders, and many more. The study concluded there’s evidence that PPARS agonists like CBD could help improve different conditions.
GPR55 Receptor: This receptor is present in the central and peripheral nervous systems. Studies show that it plays a role in various areas, including neuropathic pain, diabetes, bone health, inflammation, and cancer.
The Endocannabinoid System
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) plays a key role in regulating various bodily processes, from mood to cognition to metabolism. In the 1990s, researchers were studying cannabinoids when they discovered the ECS. Since then, this system has been the center of different scientific studies.
The function of the ECS is to maintain homeostasis in our bodies. When your body is subjected to physical or mental stress, for example, it works to promote balance. Think of it as a traffic control cop who regulates the activity of any system that needs regulation.
Further, the ECS consists of receptors, endocannabinoids, and enzymes. Initially, scientists thought that the receptors were only present in the brain. But continuous research showed there are endocannabinoid receptors throughout our bodies.
The receptors of the ECS are cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1) and type 2 (CB2). CB1 receptors are primarily present in the central nervous system, while CB2 receptors are mainly in the peripheral nervous system.
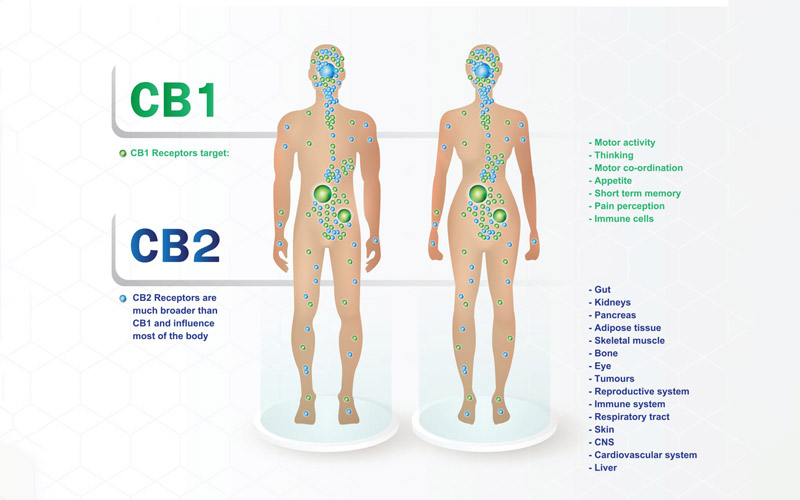
What are the Effects of CBD?
Due to CBD’s interaction with various receptors, it produces several effects on the body. Some of the conditions people use CBD for include:
- Pain
- Inflammation
- Seizures
- Stress
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Sleep problems
- Autoimmune diseases
Pain Relief: One of the popular uses of CBD is to decrease pain. CBD is a well-known analgesic. But how does CBD work in the human body for pain relief?
Some studies show it binds to the TRPV1 receptor. This interaction prevents the receptor from developing a strong response to pain.
People use CBD for various pain conditions, such as acute pain, chronic pain, muscle soreness, migraine, etc. CBD has also shown to be a possible management option for neurological issues like fibromyalgia.
Reduced Inflammation: CBD also works as an effective anti-inflammatory substance. That is why people use it for inflammatory ailments, such as joint pain, back pain, and fever. CBD relieves inflammatory tissues by decreasing the amount of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Promotes Sleep: Regulation of our sleep-wake cycle is one of the functions of the ECS. CBD complements the functions of the ECS, and by so doing, it helps improve sleep. Additionally, low CBD intake causes wakefulness, whereas high CBD intake before bed improves sleep.
Researchers have not yet discovered how CBD works for sleep. However, CBD works for people with different sleep disorders.
Regulates Immune Activities: CBD also regulates immune response by interacting with different receptors. Some of these receptors are CB, FAAH, TRPV1, and others. So, how does CBD work in the body to regulate immunity? The short answer is inflammation.
For example, when you cut a finger, several immune cells start attacking bacteria under the skin. CBD reduces the number of pro-inflammatory cytokines. So, it promotes recovery. However, it also weakens immune activities.
This effect of CBD is sometimes good and other times, undesirable. For instance, it’s beneficial to people with autoimmune diseases like arthritis. In this type of health condition, the body’s immune cells attack its own tissues. But, with CBD’s immune regulation, people with these autoimmune conditions can live better.
How Long Does It Take for CBD to Work?
So, you may be wondering: how long does CBD take to work?
How long it takes CBD to work depends on factors such as the method of ingestion and your body chemistry. Also, the condition you’re trying to manage influences how long it takes the CBD to work.
For instance, if you’re taking CBD oil for a mild headache, you’ll likely feel better faster than someone using CBD for a chronic pain condition.
When it comes to the method of ingestion, smoking or vaping produces the fastest effect. You begin to notice it almost immediately.
Another method that provides quick effects is sublingual – under the tongue. You should notice results in about 15 minutes.
Wait for about an hour for topical CBD products. Also, when you use edible CBD or consume it orally, the effects take time to kick in. You may start to feel the impact after two hours or more.
Moreover, when the effects of CBD kick in, it can last between two to six hours.
Possible CBD Side Effects
CBD is a generally safe compound. However, there are possible side effects associated with its use. Some users report the following side effects:
- Dry mouth
- Diarrhea
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Changes in weight
- Changes in appetite
These side effects are usually mild and not often a cause for concern. What’s more, research shows that CBD interacts with some medications. Therefore, you want to speak with a healthcare professional before adding CBD to your routine, especially if you’re on meds.
Can CBD and THC Work Together?
A school of thought believes CBD blocks the activity of THC, thereby reducing its psychoactive effects. The theory that CBD blocks THC is a simple way to describe how these compounds work. CBD and THC affect different receptors in the body and work quite differently.
Rather than outrightly blocking THC, CBD competes with THC. They also work in tandem with each other. For example, THC is a CB1 receptor agonist. So, it binds to this receptor to exert certain effects. However, CBD works indirectly with CB1 and CB2 receptors.
Studies show that CBD is a negative allosteric receptor modulator to the CB1 receptor. That means that although it doesn’t bind to CB1, CBD changes the shape of this receptor. This modulation weakens the way the CB1 receptor binds with THC. As a result, CBD inhibits THC’s intoxicating effects.
The Entourage Effect
The entourage effect proposes that CBD works better when you take it together with other phytocannabinoids and terpenes. On its own, CBD may not be as effective, or you may need higher doses for certain conditions. However, combining CBD with terpenes and THC – even in trace amounts – provides increased benefits.
That said, some people use CBD products because they want to avoid THC. If your goal is to experience the effects of CBD without any form of THC, stick with pure CBD.
Final Thoughts
CBD, short for cannabidiol, interacts with the endocannabinoid system to exert its many effects. There is still so much to learn about the ECS. However, CBD’s interaction with this system is beneficial in managing different symptoms and conditions.
CBD also interacts with many other receptors in the body, including those regulating immune response and pain perception. Because of these different interactions, CBD can provide support to the body.
There’s a lot we don’t know about CBD yet. But, what we know from current studies is that it’s a possible treatment option for many ailments.
