
Most of us know about the systems in the human body, such as the nervous and digestive systems. However, only a few might have heard about the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS). Discovered only recently, the ECS regulates critical bodily processes like memory, mood, cognition, and immune responses.
Apart from the role the ECS plays in different body functions, it also interacts with cannabinoids. Although the discovery of this system is relatively new, scientists have been learning more about it. In this article, we will discuss the endocannabinoid system, how it works, and why it needs cannabinoids like CBD.
What is the Endocannabinoid System?
First, let’s look at the term endocannabinoid. Endo is short for endogenous, meaning produced within the body. Cannabinoid comes from the word cannabis. Therefore, endocannabinoid is a cannabis-like substance that is naturally present in the body.
Now, what is the endocannabinoid system?
The endocannabinoid system, or ECS, is a cell-signaling system that plays a crucial role in the body. It consists of receptors present throughout the body: brain, glands, organs, and more. Although the ECS performs different functions in these parts, the end goal is always homeostasis.
What does the endocannabinoid system do? Scientists are still trying to understand the endocannabinoid system. However, current studies show that it plays a role in regulating multiple body functions, including:
- Mood
- Cognition
- Immune activities
- Sleep
- Appetite
- Memory
- Fertility and reproductive system function
- Motor control
Parts of the ECS
The endocannabinoid system has three parts, namely:
- Cannabinoid receptors
- Endocannabinoids
- Enzymes
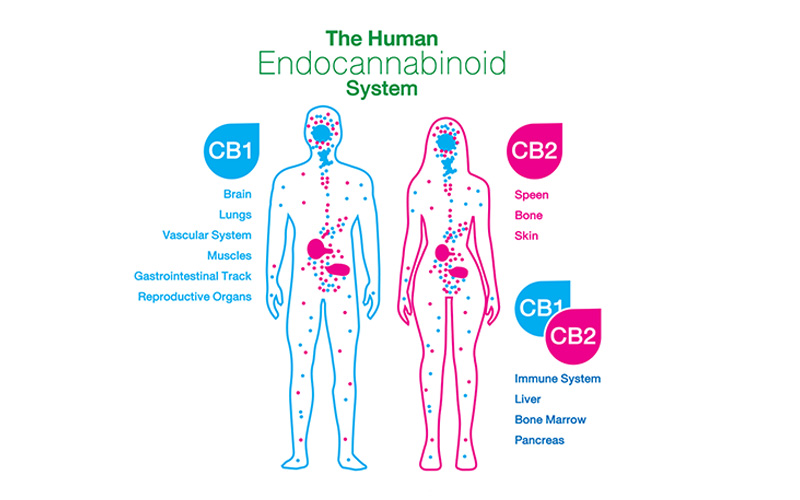
Cannabinoid Receptors: These receptors are present throughout the brain and body. There are two types, which are the CB1 receptor and CB2 receptor. CB1 receptors are mostly present in the central nervous system. CB2 receptors are found predominantly in the peripheral nervous systems, particularly immune cells.
Endocannabinoids: Our bodies produce their own cannabinoids, called endocannabinoids. The two most researched endocannabinoids discovered so far include anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglyerol. They help the body’s internal functions to operate smoothly.
Enzymes: Enzymes are another part of the ECS. Their function is to break down the endocannabinoids after they carry out their roles. Two main enzymes in the ECS are:
- Fatty acid amide hydrolase is responsible for breaking down anandamide
- Monoacylglycerolacid lipase, which breaks down 2-arachidonoylglyerol
How Does the Endocannabinoid System Work?
So, how does the endocannabinoid system work? According to Harvard Health, the ECS works by regulating different bodily processes.
It acts like a traffic control cop to keep the body in balance. This system regulates activities via immediate feedback. It turns down or up the activity of any system that is out of balance and needs to be regulated.
Our body’s endocannabinoids stimulate the receptors of the endocannabinoid system. Interestingly, cannabinoids from the cannabis plant have a similar structure to endocannabinoids.
When an endocannabinoid binds to a receptor, it can result in different effects depending on the location of the receptor. The effect you get also depends on which endocannabinoid binds to the receptor.
For instance, if an endocannabinoid binds to a CB1 receptor in the spinal cord, the result could be pain relief. Also, it can bind to CB2 receptors in your immune cells to notify the body of inflammation.
What’s more, the endocannabinoid system also uses CBD, THC, and other cannabinoids to function.
CBD and Cannabinoids
Experts are not fully sure how CBD and the endocannabinoid system interact. However, they know it doesn’t bind to CB1 and CB2 receptors. Instead, many scientists believe that CBD works by supporting the ECS.
So, how does CBD affect the endocannabinoid system? It prevents the endocannabinoids from breaking down. Others believe that CBD bind to receptors that are not cannabinoid receptors.
Experts are researching other ways cannabinoids work with the body’s endocannabinoid system. While these studies are still ongoing, research shows that cannabinoids interact with the ECS for improved body benefits.
Furthermore, CBD is the most popular compound in cannabis. It’s also the most well-researched. But, that doesn’t mean that there aren’t any other compounds in cannabis or hemp plants.
For instance, we also have other cannabinoids like THC, CBN, CBG, and so on. In fact, the cannabis plant has over a hundred chemical compounds.
Why the Endocannabinoid System Needs Cannabinoids
You may be wondering why the endocannabinoid system needs cannabinoids. The receptors of the endocannabinoid system play vital roles in the body. However, they cannot function alone. These receptors need cannabinoids to regulate different bodily processes.
As mentioned earlier, the body produces its cannabinoids. But studies show that some people may be deficient. That is why we can consume cannabinoids with the help of cannabis products. When you take cannabinoids like CBD and THC, they interact with these cannabinoid receptors in the ECS.
The endocannabinoid system is intelligent and distributes cannabinoids to different areas when needed. Also, cannabinoids are nontoxic.
When not needed, the body can store them. So, it’s impossible to consume a lot to build up a toxic level in your system
How THC Interacts with the ECS
Let’s look at how THC affects the endocannabinoid system. THC interacts with the endocannabinoid system by binding to CB receptors. So, it interacts with the ECS as the endocannabinoids do. THC is a powerful cannabinoid because it binds to and stimulates both CB1 and CB2 receptors.
Supporting the Endocannabinoid System with Hemp
Given the information we have about the endocannabinoid system, it makes sense to support it with cannabis. So, how do you go about supporting the endocannabinoid system with hemp and cannabis? You can start by sourcing quality CBD products from reliable brands in the industry.
Many aspects of CBD products determine how well they can affect the ECS and bring desired results. For instance, organic hemp plants are more beneficial because they have not been exposed to toxic chemicals. These toxins can degrade cannabinoids. Not only that, but they are unsafe for human consumption.
Further, manufacturers use different extraction processes when creating CBD products. The best method by far is CO2 extraction. This process is safe and also preserves the quality of the cannabinoids.
You can consume CBD daily to give the endocannabinoid system as much support as possible. Cannabinoids work cumulatively. Therefore, one of the ways to ensure the ECS gets the best support is by taking cannabidiol consistently.
Endocannabinoid Deficiency
Some scientists believe in a theory called clinical endocannabinoid deficiency (CECD). This theory hypothesizes that low levels of endocannabinoids in the body lead to the development of ailments.
A 2016 review of over ten years of research suggests that the theory could explain why people have diseases such as fibromyalgia. Migraine and irritable bowel syndrome are other conditions mentioned in the review.
None of these ailments have a clear root cause. Experts are yet to define their underlying causes. Endocannabinoid deficiency is not an illness. However, it’s the term for ailments with that common feature.
Some of these conditions usually involve more than one system. It’s not surprising when you look at the areas ECS influences.
For instance, fibromyalgia generally involves the immune system, digestive system, central and peripheral nervous system, and endocrine system. That seems like it’s a lot of unrelated systems until you look at the endocannabinoid system and homeostasis.
We’re still at the early stage of figuring out the endocannabinoid system and endocannabinoid deficiency. However, with the increasing popularity of CBD and cannabis plants, we’ll most likely see more research.
The Endocannabinoid System in Pets
Now, let’s discuss the endocannabinoid system in pets. While shopping for your CBD products, you’ll probably come across CBD for pets. Most pet owners are interested in improving the wellness of their cats and dogs with cannabis products.
Studies show that the endocannabinoid system is present in mammals, including cats, dogs, and some other animals. So, it’s likely that your pets will enjoy the same benefits and functions of the ECS the same way you do.
When using CBD for your pets, there are crucial things to note. First, your four-legged companion needs different milligrams than you do. They have different weights, so give them these products based on size. Top CBD brands creating pet CBD products also offer dosing guidelines. Be sure to pay attention to that and follow the instructions.
Also, don’t give your pet your CBD. There’s a reason companies produce pet-specific products. Lastly, you don’t want your pet consuming THC. Their bodies respond differently to THC intake compared to us. So, it may be toxic to your dog or cat when they ingest THC.
Final Thoughts
The endocannabinoid system helps keep the body’s internal processes in balance. There are a lot experts don’t know yet about the ECS. However, studies suggest that the ECS plays a role in maintaining balance in the body.
The ECS consists of cannabinoid receptors, endocannabinoids, and enzymes. All these work together for the proper functioning of the body and to maintain balance in physiology processes. Some of the processes the ECS helps regulate include mood, sleep, appetite, digestion, learning, and memory.
Cannabis products may help you optimize your endocannabinoid system. It’s essential to remember that supporting your ECS with cannabinoids doesn’t cure all your ailments. Like most physiological processes, it’s complex, and there’s so much we don’t know about the ECS.
